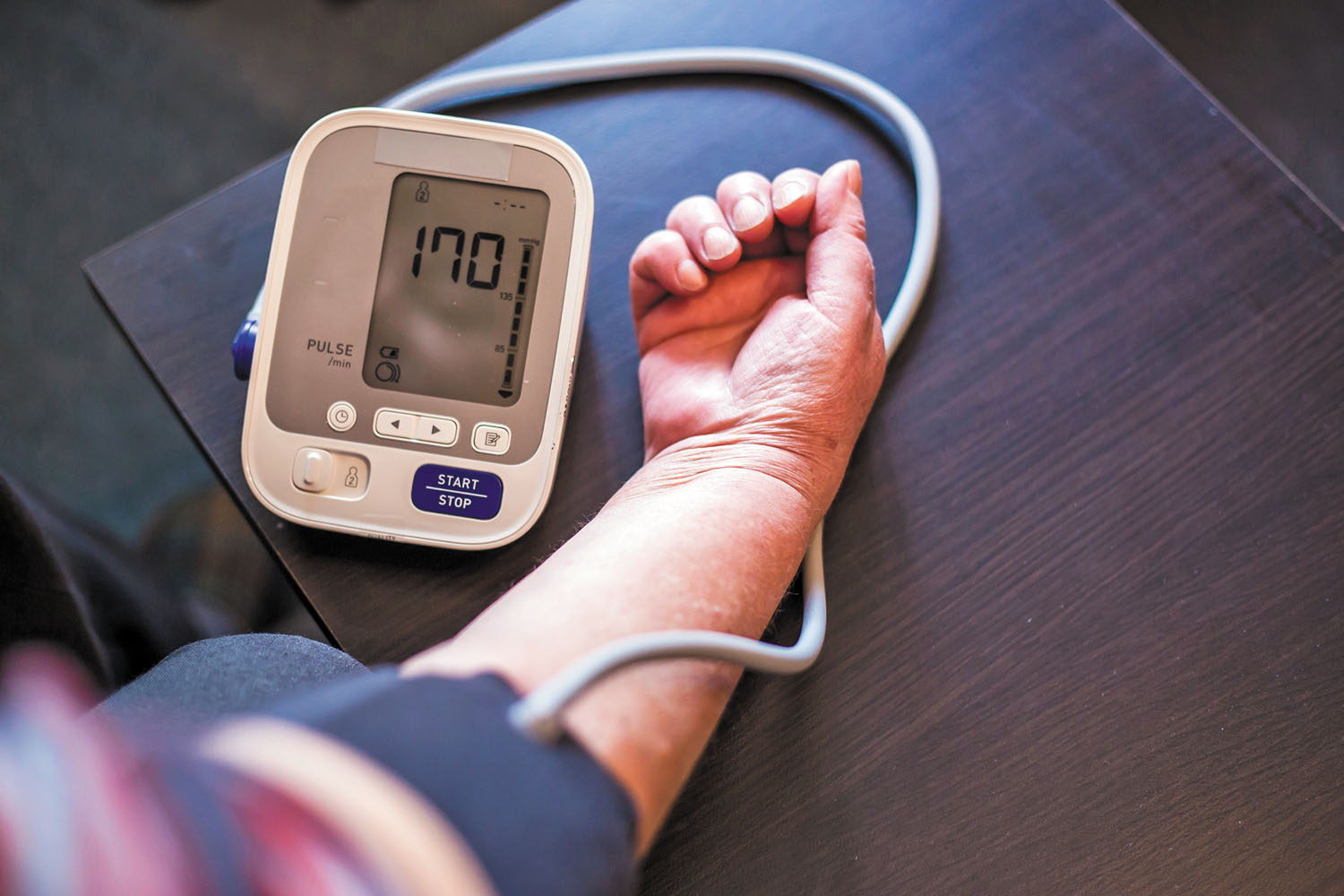
High blood pressure or Hypertension is dangerous because it can cause stroke, heart attack, heart failure, or kidney disease. Treatment of hypertension aims to reduce high blood pressure and avoid damage to vital organs, such as the brain, heart, and kidneys. According to research, treatment for hypertension is associated with a decrease in stroke (an average of 35% –40%), heart attack (20% –25%), and heart failure (more than 50%). More than 130 are classified as systolic blood pressure and over 80 as diastolic.
Everyone should be encouraged to make lifestyle changes to prevent high blood pressure, such as eating a healthy diet, quitting smoking and exercising more. Treatment with medication is recommended in people over 65 years of age with blood pressure below 130/80 and risk factors such as diabetes and high cholesterol.
Lifestyle Changes to Treat High Blood Pressure
A critical step in preventing and treating high blood pressure is a healthy lifestyle. You can lower your blood pressure with the following lifestyle changes:
- Losing weight if you are overweight or obese
- Quitting smoking
- Eating a healthy diet, including the DASH diet (eating more fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products, less saturated and total fat)
- Reducing the amount of sodium in your diet to less than 1,500 milligrams a day if you have high blood pressure; healthy adults should try to limit their sodium intake to no more than 2,300 milligrams a day (about 1 teaspoon of salt).
- Getting regular aerobic exercise (such as brisk walking at least 30 minutes a day, several days a week)
- Limiting alcohol to two drinks a day for men, one drink a day for women.
Drugs to Treat High Blood Pressure
There are several types of drugs used to treat high blood pressure, including:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)
- Diuretics
- Beta-blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Alpha-blockers
- Alpha-agonists
- Renin-inhibitors
- Combination medications.