Angioplasty is a procedure that improves blood flow to the heart. This opens a coronary supply route that was limited or interrupted due to a heart attack. The coronary artery may be obstructed by blood coagulation and ruptured plaque of calcium and fat causing a heart attack. After a heart attack, specialists perform angioplasty as soon as possible. But this procedure is not available in many hospitals. If a patient is in a hospital that does not provide angioplasty treatment, they may be referred to another hospital where angioplasty is possible.
Why Do Coronary Angioplasty And Stents
In general, angioplasty or without stenting is the primary decision in treatment after a heart attack. Visit a complex angioplasty specialist in Jaipur.
Despite Numerous Things Are Included, Angioplasty May Be Done Which Are:
- Heart Attack.
- Have severe and frequent angina that isn’t reacting to drugs and way of life changes.
- Have an indication of extremely lessened blood flow known as ischemia to a region of heart muscle caused by at least one narrowed coronary corridors.
- Have a blocked or narrowed artery that is probably going to be dealt with successfully with angioplasty.
- Are in good wellbeing to have the method.
Angioplasty May Not Be A Primary Treatment Choice, Reasons are:
- There is no indication of decreasing the flow of blood to the heart muscle.
- Just little zones of the heart are at risk, and you don’t have incapacitating angina side effects.
- You are in issues for having issues such as dying amid angioplasty because of other medical issues.
- You can’t take blood thinner drugs, headache medicine (aspirin) and another antiplatelet, subsequent to getting a stent.
- The influenced artery can’t become to amid angioplasty.
How Is Angioplasty Done?
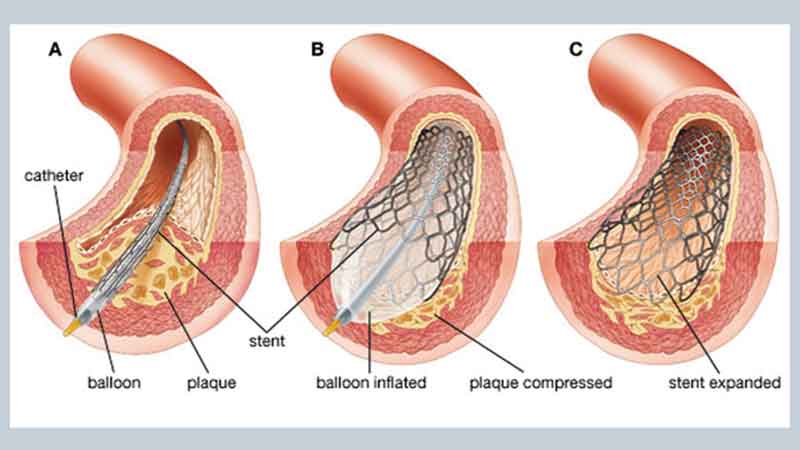
Angioplasty ends by using a thin, delicate tube called a catheter. A specialist embeds a catheter in a vein in the wrist or groin. The specialist intentionally directs the catheter through the vein until it receives the coronary arteries on the heart. Here we are discussing coronary angioplasty and stents. Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao is the best heart expert in India. Cardiac catheterization is also called a coronary angiogram. Your specialists first use a catheter to search for coronary vein obstruction or narrowing. It ends by injecting a dye that contains iodine in the veins. The dye makes coronary veins noticeable on a computerized X-beam screen. This test is also called a coronary angiogram. In most cases, the specialist may exclude loose pieces of blood clots from the arteries of the heart. It ends with a small gadget that looks like a vacuum. The specialist moves the gadget through a catheter into the blocked heart artery and removes the coagulation pieces. This is the latest procedure that can be used nowadays during angioplasty.
Risks Of Angioplasty Involve:
- Bleeding at the cut site.
- Damage to the vein at the cut site.
- Sudden closure of the coronary vein.
- Little tear in the internal layer of the heart artery.
- Chances of Heart Attack.